beginning
In this article, I will explain the “cervical spine” in detail.
The cervical spine is known as the neck bone and is responsible for the flexibility and support of the human neck. In this article, I will explain the structure and function of the cervical spine, common diseases related to the cervical spine, and their treatments. We will also introduce preventive measures and exercises to protect the cervical spine in everyday life. Please use this article to deepen your understanding of the body.
Click here to watch a video about the cervical spine
teamLab Body Pro Free Download
A 3D anatomy app that shows all the structures of the human body
Download teamLab Body Pro here!
What is the cervical vertebra
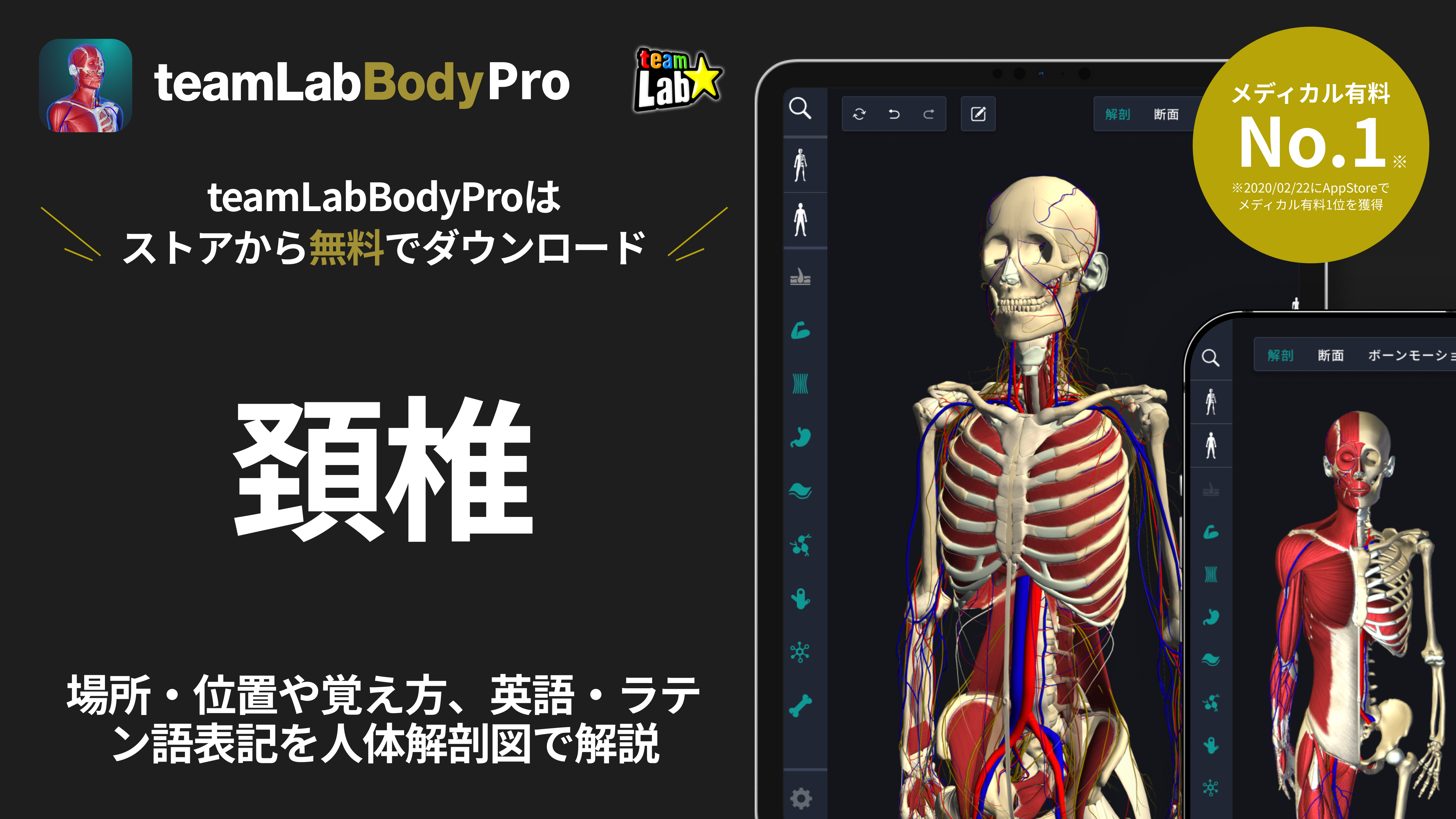
The cervical spine refers to the vertebrae located in the neck of the human body. It plays an important role in supporting the head and enabling neck movement in various directions. It is one of the most mobile regions throughout the body. Let's explain these functions and structures in detail through human anatomy diagrams.
How to read cervical spine
Cervical spine is read as “tight” in Japanese. The Chinese character “” is used to represent the neck or throat, and “spine” means vertebrae or spine. Therefore, cervical spine is a word that literally indicates a “neck bone.”
Characteristics of the cervical spine
The cervical spine is located at the top of the human spine and usually consists of 7 vertebrae. These are numbered C1 to C7, and the top two, called C1 (atlas) and C2 (axis), play a particularly important role in neck mobility. In particular, the shape of C1 and C2 is very different from other vertebrae, and they are designed to support head rotation.
Location and position of the cervical spine
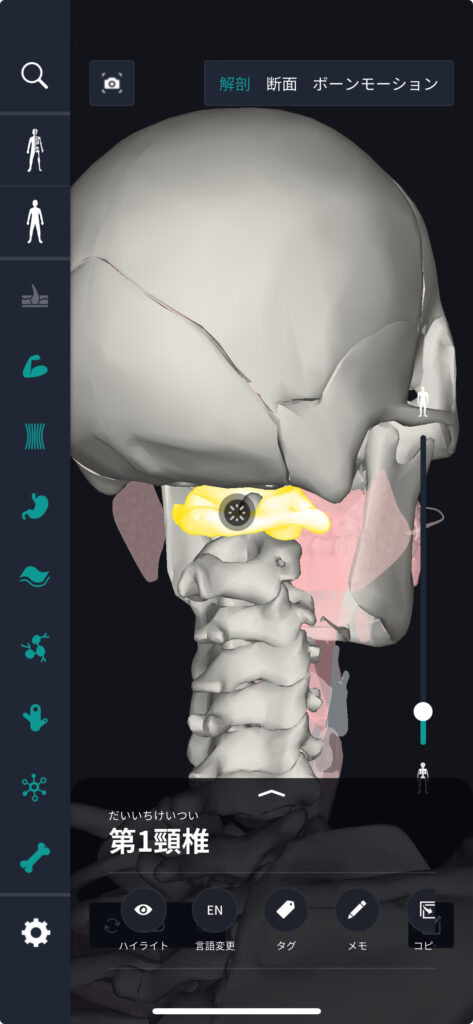
The cervical spine is located below the head, at the top of the spine, and continues with the thoracic spine. When viewed from the front, it is slightly behind the center of the neck. In human anatomy diagrams, this complex structure is depicted in detail, making it easier to understand how it contributes to neck movement.
(There are several cervical vertebrae, and the first cervical vertebra is shown in the figure.)
How to memorize cervical vertebrae
It is common to remember the cervical vertebrae as “7 from C1 to C7.” Among these, if you remember “C1 is Atlas and C2 is Axis,” you can suppress the two vertebrae that are particularly important in the cervical spine. Also, if you memorize the cervical spine with the phrase “the 7 vertebrae that make up the neck,” it will be easier to imagine.
English and Latin for cervical spine
Cervical vertebrae is expressed as “Servical Vertebrae” (Servical Vertebrae) in English, and “Vertebrae Cervicales” in Latin. Here, “cervical” means “neck,” and “vertebrae” means plural vertebrae.
Trivia about the cervical spine
The main nerves and blood vessels that pass through the cervical spine extend to the head and upper limbs, and abnormalities in this area can cause various symptoms such as neck pain and numbness in the hands and feet. Also, the cervical spine is an area that is easily damaged by accidents and injuries, so care must be taken in everyday life.
Tissues associated with the cervical spine: characteristics of the vertebral body
The vertebral body forms each bone in the spine, and the cervical spine has several unique characteristics compared to other parts of the spine. First, the cervical spine is composed of 7 vertebrae from C1 to C7, and each has a different shape and function. For example, C1 (Atlas) supports the head, and C2 (axis) has the role of rotating the head. Also, the vertebral body of the cervical spine is smaller than the vertebral bodies in other parts of the spine, and has more articular surfaces to enable fine movement.
Tissues related to the cervical spine: location and position of the vertebral body
The cervical spine is located behind the neck, from the bottom of the head to the thoracic spine. C1 is at the top, and numbers are numbered from here down to C7. The shape of the cervical vertebral body is flat at the top and bottom, and slightly convex back and forth. This makes it possible to smoothly perform complex movements such as forward bending, backward bending, side bending, and rotation of the neck.
Tissues associated with the cervical spine: trivia about the vertebral body
The first cervical vertebra (atlas) and the second cervical vertebra (axis) have clearly different structures from other vertebrae, enabling flexible movement of the neck and head support.
The cervical spine is one of the areas of the spine most prone to wear and tear in a normal person's life. This is because the cervical spine constantly supports the heavy head and needs to move in multiple directions.
A herniated cervical disc may cause neck pain, numbness in the hands and feet, and muscle weakness. In order to maintain the health of the cervical spine, it is important to maintain proper posture and perform regular exercise.
The cervical spine and the vertebral bodies that make it up play a very important role in making our daily lives comfortable. Protect the health of your cervical spine with proper care and achieve a comfortable life over a long period of time.
Cervical spine quiz and correct answers
Q1. How many vertebrae does the human cervical spine usually consist of?
A1. 7
Q2. Which cervical vertebra plays a particularly important role in head rotation?
A2. C1 (Atlas) and C2 (Axis)
summary
This time, I explained the location and location of the “cervical spine,” how to memorize it, and the English and Latin notation.
How was it?
I would be happy if reading this article deepened my understanding of anatomy.
Learning is a long, never-ending journey, but I sincerely wish you all the best. Let's continue to study together and work hard for the national exam!
Please look forward to the next blog.
Learn more with the anatomy app “TeamLabBody Pro”!
teamLabBody Pro is a “3D human anatomy application” that covers the entire body of the human body, including muscles, organs, nerves, bones and joints.
The human body is faithfully reproduced from CT and MRI data based on data from multiple subjects. Since medical book-level content supervised by physicians can be freely viewed from all angles, it can be used in various medical situations, such as explaining surgery to patients and studying anatomy for students.
If you want to see the parts introduced this time in more detail, please download the anatomy application “teamLabBody Pro.”
teamLab Body Pro Free Download
A 3D anatomy app that shows all the structures of the human body
Download teamLab Body Pro here!