beginning
In this article, I will explain effective study methods, starting with knowledge of specialized parts in human anatomy.
In human anatomy, it is necessary not only to memorize the names of various organs, muscles, and bones, but also to remember where they are located in the body. Therefore, it is necessary to learn as efficiently as possible.
I hope you will deepen your understanding even a little by reading this article and using the app.
Now, I will explain the details about “cervical hemispinus muscle and thoracic hemispinus muscle” and how to study human anatomy.
teamLab Body Pro Free Download
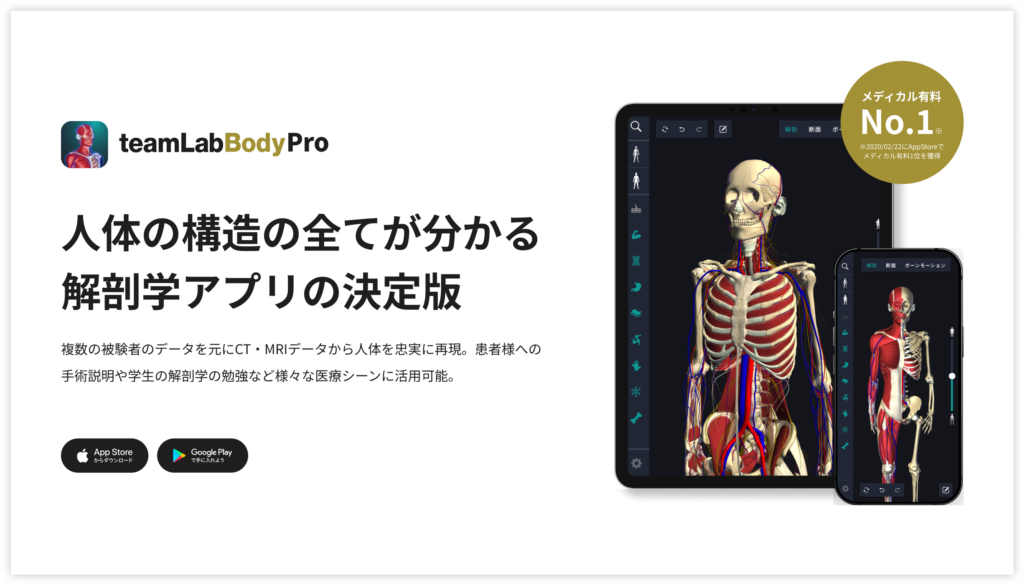
A 3D anatomy app that shows all the structures of the human body
Download teamLab Body Pro here!
What are cervical hemispinatus muscle and thoracic hemispinatus muscle?
The anatomy application allows you to view a selection of anatomy 3D models. In this model, there are various observation methods such as surfaces, cross-sections, and nervous systems. This time, I'll explain using an anatomy application.
About semispinatus cervicus muscle

Semispinalis cervicis (semispinalis cervicis) is a muscle located deep in the back and plays an important role in cervical spine movement. This muscle starts from the spines in the upper thoracic spine (T1-T6) and stops at the spines in the cervical spine (C2-C5). The semispinatus cervicus muscle is involved in backflexion, rotation, and lateral flexion of the spine, and mainly supports neck movements.
The cervical semispinatus muscle works actively in movements that tilt the head and neck backwards (backward bending), side bending, and rotation movements. It is also important for maintaining posture, and is an essential muscle for maintaining neck stability. If these muscles are not working properly, neck range of motion may be limited or poor posture may occur. Strengthening the cervical semispinatus muscle and keeping it flexible is very effective for maintaining neck health.
Study points
Anatomical understanding
Semispinalis cervicis is a muscle that is part of the deep dorsal muscle group and is mainly associated with the cervical spine. When learning this muscle, it is important to first understand its anatomical location. The cervical semispinatus muscle starts at the top of the thoracic spine and stops at the spiny process at the top of the cervical spine. Specifically, it starts from the spines (T1-T6) in the upper thoracic spine and attaches to the C2 to C5 spines in the cervical spine.
In order to advance learning, it is important to accurately grasp the direction in which the muscles run and understand the relationships with neighboring muscle groups (e.g. trapezius muscle, semispinatus cephalospinus muscle group, etc.). In order to deepen anatomical understanding, it is effective to use a 3D application or anatomical diagram to visually confirm muscle position and movement. Also, in order to understand how the cervical semispinatus muscle works, it is important to learn about the anatomy of the spine and cervical spine, and to know how those muscles contribute to posture retention and movement.
Understanding muscle function
Functional understanding of the cervical semispinatus muscle is important to focus primarily on its role in neck movement. This muscle mainly bends the cervical spine backwards, and is also involved in rotation and side bending. It supports neck movement and plays an important role in maintaining posture. In particular, understanding how the cervical semispinatus muscle works when performing neck rotation or backward bending movements will lead to an improvement in actual movement.
In order to deepen functional understanding, it is effective to actually perform rotation and backward bending exercises and be aware of how the cervical semispinatus muscle works at that time. Also, since it is a muscle that contributes to improving posture and preventing neck pain, it is possible to apply these elements to daily life and training.
Practical applications
In order to utilize the cervical semispinatus muscle in actual training, it is important to perform exercises that increase neck flexibility and muscle strength. For example, by incorporating stretches and exercises (neck stretches, shoulder rotation exercises, etc.) involving backward bending and rotation of the neck, muscle strength improvement targeting the cervical semispinatus muscle can be expected. Also, when taking the same posture for a long time in daily life, it is also effective to move your neck regularly and activate the cervical semispinatus muscle.
About thoracic semispinatus muscle

The semispinalis thoracis muscle (Semispinalis thoracis) is located in the deep muscle group of the back and contributes to the stability of the thoracic spine. This muscle starts from the spines in the lower thoracic spine (T6-T10) and stops at the spines in the upper thoracic spine (T1-T6). The thoracic semispinatus muscle is involved in backflexion, rotation, and lateral bending of the thoracic spine, and is particularly responsible for increasing spinal stability.
The thoracic semispinatus muscle expands the range of motion of the spine and also contributes to maintaining posture and improving chest flexibility. If this muscle is not working enough, poor posture or reduced motor function may occur. Strengthening and keeping the thoracic semispinatus muscle flexible is very important for maintaining back and chest health.
Study points
Anatomical understanding
The semispinalis thoracis muscle (Semispinalis thoracis) is part of the deep muscle group and is mainly associated with the thoracic spine. When learning this muscle, it is essential to first understand its anatomical location. The thoracic semispinatus muscle starts from the spines in the upper thoracic spine and stops at the spines in the lower thoracic spine. Specifically, it starts from T6 to T10 spines and stops at T1 to T6 spines.
As a first step in learning, it is important to accurately grasp the direction in which the thoracic hemispinatus muscle runs and understand the positional relationship with neighboring muscle groups (e.g. latissimus dorsi muscle, trapezius muscle, etc.). In order to advance visual learning, it is important to check muscle movement using anatomical diagrams and 3D apps, and clarify the function and role of each part. Also, in order to learn how the thoracic semispinatus muscle stabilizes the spine, it is a good idea to understand the structure of the spine and thoracic spine.
Understanding muscle function
For a functional understanding of the thoracic semispinatus muscle, it is important to understand its role in stabilizing the thoracic spine. This muscle works by flexing the thoracic spine backwards, aiding rotation, or supporting lateral spine bends. Since it is involved in chest exercises and helps stabilize posture, understanding how the thoracic semispinatus muscle supports the spine leads to actual exercise and posture improvement.
In order to deepen functional understanding, it is a good idea to proceed with learning while being aware of how the thoracic semispinatus muscle works in exercises to move the thoracic spine and maintain posture. Also, it is important to learn while realizing how strengthening the thoracic semispinatus muscle contributes to improving posture and chest flexibility.
Practical applications
In order to utilize the thoracic semispinatus muscle in actual training, thoracic spine and back training is effective. For example, by incorporating back and chest stretches and exercises (back bending exercises, thoracic rotation exercises, etc.), improvements in muscle strength and flexibility targeting the thoracic semispinatus muscle can be expected. It is also beneficial to consciously improve posture and activate the thoracic semispinatus muscle in everyday life.
How to study human anatomy
I will explain specific study methods using human anatomy applications.
Check your past learning history and practice repeatedly
Here are the steps to check your anatomy learning history and practice iteratively effectively.
1. Check your learning history in the app
Reviewing your learning history with the application is an important step in effectively advancing anatomy learning. First, launch the app and go to the learning history section from the main menu. Many anatomy apps are designed to show your progress in the form of graphs and lists, so you can visually check which parts you've learned about and how much time you've spent.
By using this data, you can understand which areas you have strengths in and where you need to spend more time and effort. We also recommend using a dedicated tag or notebook function to mark areas you are particularly weak at or where you need to relearn. Regularly checking your learning history and looking back on past learning content will lead to efficient review and deepening understanding.
2.Make a plan for iterative learning
Making an efficient repetitive learning plan based on learning history is extremely effective in promoting knowledge retention. First, identify weak points and areas where you need to relearn. Next, arrange these study items into a weekly or monthly calendar and create a specific study schedule. By proceeding in a planned manner, you can learn each part evenly and avoid packing in a large amount of information at once.
Using a task management app or digital calendar to set study reminders is effective. Also, it's important to have the flexibility to regularly review progress and revise plans as needed. By having goals and proceeding with your studies in a planned manner, you can efficiently acquire anatomical knowledge.
3.Use 3D features to learn visually
By utilizing the 3D function, learning anatomy is easier to understand visually. The 3D model shows the structure of the human body three-dimensionally, and each part can be observed in detail. This makes it possible to intuitively grasp positional relationships between deep muscles and organs that are difficult to capture in a planar view. For example, you can learn even the smallest details by rotating specific muscles and bones and zooming in and out.
Also, there are many apps that have the function of displaying cross-sectional views of each part using a 3D model, which is useful for deepening understanding of internal structures. This diversity of visual information helps with memory retention and improves immediate responsiveness in tests and practice situations. By utilizing the 3D function and learning visually, you can learn anatomy knowledge more deeply and efficiently.
Use the memo function concretely
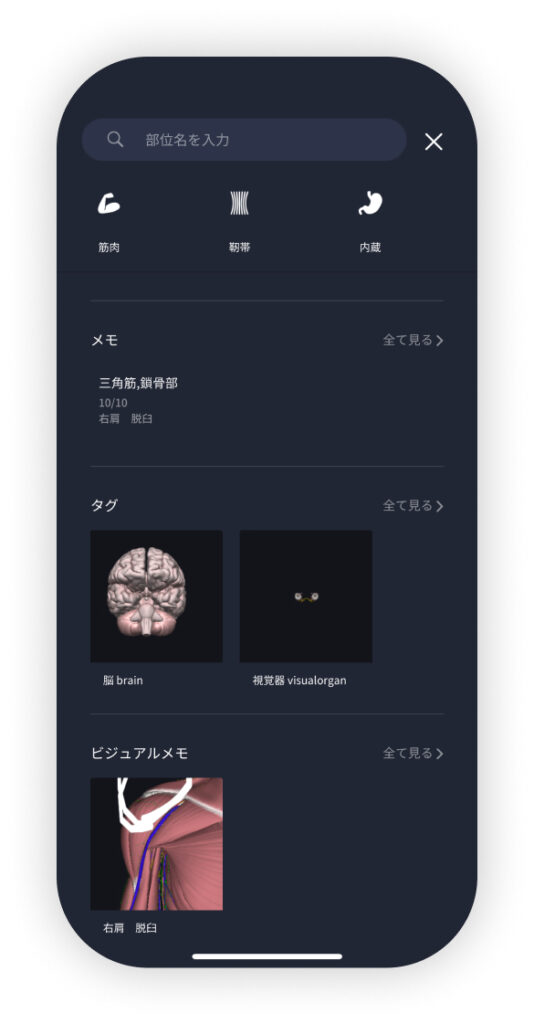
Make notes so you don't forget the things and points you've noticed while studying. The memo function can be used for different purposes, such as inputting text, saving images, and writing memos. Tag your notes to make them easier to review later.
Test your learning regularly in the form of quizzes
Regularly testing what you've learned in a quiz format is a very effective way to anchor your anatomy knowledge. Quiz-style tests help you objectively grasp your level of understanding and areas you lack while repeating knowledge.
For example, by using a learning app to conduct quizzes every specific period, you can reconfirm what you've learned and strengthen your memory. There are a wide range of quiz formats, such as multiple choice questions, fill-in-the-blank questions, and short answer questions, and each helps understanding from a different angle and develops the ability to utilize various types of knowledge.
Get feedback
If possible, get feedback from other learners and experts. It helps you find your own gaps in understanding and areas for improvement. You can also keep yourself motivated to learn by regularly testing yourself. Feeling a sense of accomplishment and progress increases motivation for continuous learning.
summary
This time, I explained how to study “cervical hemispinatus muscle/thoracic hemispinatus muscle” using an application!
Thank you for reading this far.
I would be happy if reading this article helped you learn about anatomy.
Learning is a long, never-ending journey, but I sincerely wish you all the best. Let's continue to study together and work hard for the national exam!
Please look forward to the next blog.
teamLab Body Pro Free Download
A 3D anatomy app that shows all the structures of the human body
Download teamLab Body Pro here!





