beginning
In this article, I will explain effective study methods, starting with knowledge of specialized parts in human anatomy.
In human anatomy, it is necessary not only to memorize the names of various organs, muscles, and bones, but also to remember where they are located in the body. Therefore, it is necessary to learn as efficiently as possible.
I hope you can read this article and use the app to deepen your understanding even a little bit.
Now, I will explain the contents of the dorsal aponeurosis and how to study human anatomy.
teamLab Body Pro Free Download
A 3D anatomy app that shows all the structures of the human body
Download teamLab Body Pro here!
What is the dorsal aponeurosis?
The anatomy application allows you to view a selection of anatomy 3D models. In this model, there are various observation methods such as surfaces, cross-sections, and nervous systems. This time, I'll explain using an anatomy application.
About dorsal aponeurosis
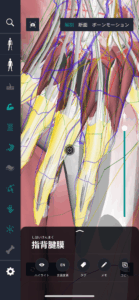
The dorsal aponeurosis (dorsal aponeurosis) is a connective tissue structure located on the dorsal side of the hand. This aponeurosis is continuous to the extensor tendon of the finger of the hand and is involved in the joint movement of the fingertips. Specifically, it plays a role in helping the interphalangeal joints (DIP and PIP) stretch. The dorsal aponeurosis is a fibrous connective tissue that stretches throughout the finger, and is also related to the left and right collateral ligaments, lateral cords, and pterygiform ligaments. These structures also play a role in reducing the load on each joint by adjusting finger movements and promoting force distribution. The presence of the dorsal aponeurosis allows the fingers to move smoothly and stably, and various detailed movements can be performed accurately.
Study points
Location and structure of the dorsal aponeurosis
The dorsal phalangeal aponeurosis is located on the back of the finger of the hand and extends specifically from the metacarpal joint (MCP) to the distal interphalangeal joint (DIP). This anatomical structure takes the form of an elongated band on the dorsal side of the finger and is characterized by shiny, fibrous tissue. The dorsal aponeurosis has fibers from the extensor tendon that spread, is arranged along the long axis of the finger, and is particularly strongly connected near the proximal interphalangeal joint (PIP). Also, the dorsal aponeurosis consists of longitudinal fibers and transverse fibers, and adjusts finger joint movement based on their respective roles. Longitudinal fibers help fingers stretch, while transverse fibers support joint stability. The structure of the dorsal aponeurosis also intersects with pterygiform ligaments and lateral cords, thereby making complex finger movements and distribution of forces possible. As a result, the dorsal aponeurosis acts as an essential component for the overall shape and function of the finger.
The role and function of the dorsal aponeurosis
The dorsal aponeurosis is an important anatomical structure responsible for finger joint movement. Its main role is to help extend the interphalangeal joints (especially PIP and DIP), and it works closely with the extensor tendons to enable this movement. The dorsal aponeurosis forms a structure where fibers branch from the distal part of the extensor tendon and cover the back of the finger and go beyond each joint. Thus, the transmission power of the tendon is efficiently transmitted to the fingertips, and the movement of grasping the target object is controlled. In addition, the dorsal aponeurosis distributes contractile force evenly to each joint, prevents finger stiffness, and also plays a role in ensuring smooth movement. Furthermore, in addition to playing a role as a fulcrum for stabilizing finger movement, the dorsal aponeurosis maintains joint and finger integrity by cooperating with the pterygium ligament and lateral cords to cushion traction forces. Due to these functions, the dorsal aponeurosis is an essential structure for maintaining normal finger functionality.
English notation for dorsal aponeurosis
The dorsal aponeurosis is called an “extensor hood” or “extensor expansion” in English. This structure is located on the dorsal side of the hand and exists in a form where the extensor tendon extends to the end of the finger. Mainly, it extends from the middle finger joint (MCP) of the finger to the distal interphalangeal joint (DIP), and since it is positioned to cover the back of the finger within this range, the name “hood (hood)” is given.
How to study human anatomy
I will explain specific study methods using human anatomy applications.
Check your past learning history and practice repeatedly
Here are the steps to check your anatomy learning history and practice iteratively effectively.
1. Check your learning history in the app
Reviewing your learning history with the application is an important step in effectively advancing anatomy learning. First, launch the app and go to the learning history section from the main menu. Many anatomy apps are designed to show your progress in the form of graphs and lists, so you can visually check which parts you've learned about and how much time you've spent.
By using this data, you can understand which areas you have strengths in and where you need to spend more time and effort. We also recommend using a dedicated tag or notebook function to mark areas you are particularly weak at or where you need to relearn. Regularly checking your learning history and looking back on past learning content will lead to efficient review and deepening understanding.
2.Make a plan for iterative learning
Making an efficient repetitive learning plan based on learning history is extremely effective in promoting knowledge retention. First, identify weak points and areas where you need to relearn. Next, arrange these study items into a weekly or monthly calendar and create a specific study schedule. By proceeding in a planned manner, you can learn each part evenly and avoid packing in a large amount of information at once.
Using a task management app or digital calendar to set study reminders is effective. Also, it's important to have the flexibility to regularly review progress and revise plans as needed. By having goals and proceeding with your studies in a planned manner, you can efficiently acquire anatomical knowledge.
3.Use 3D features to learn visually
By utilizing the 3D function, learning anatomy is easier to understand visually. The 3D model shows the structure of the human body three-dimensionally, and each part can be observed in detail. This makes it possible to intuitively grasp positional relationships between deep muscles and organs that are difficult to capture in a planar view. For example, you can learn even the smallest details by rotating specific muscles and bones and zooming in and out.
Also, there are many apps that have the function of displaying cross-sectional views of each part using a 3D model, which is useful for deepening understanding of internal structures. This diversity of visual information helps with memory retention and improves immediate responsiveness in tests and practice situations. By utilizing the 3D function and learning visually, you can learn anatomy knowledge more deeply and efficiently.
Use the memo function concretely
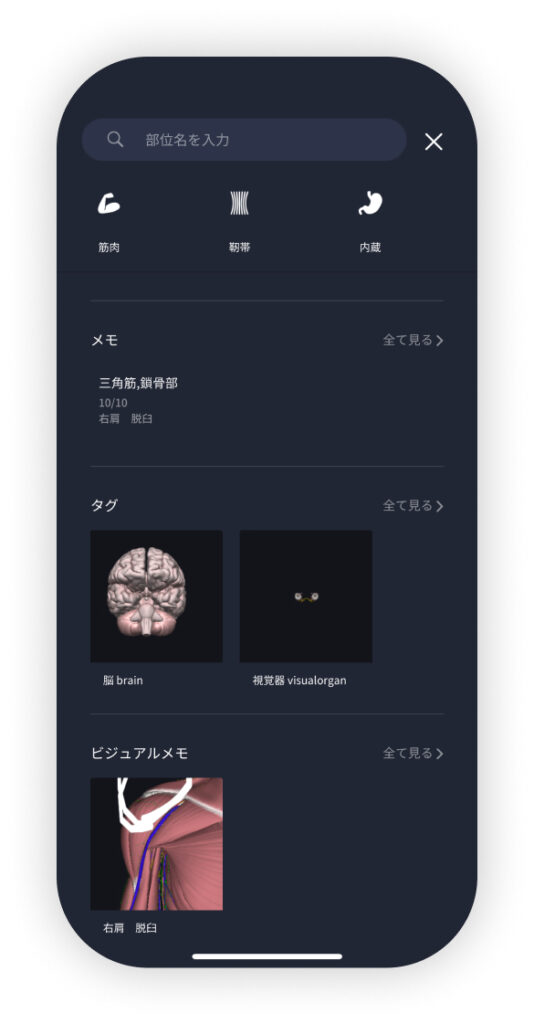
Make notes so you don't forget the things and points you've noticed while studying. The memo function can be used for different purposes, such as inputting text, saving images, and writing memos. Tag your notes to make them easier to review later.
Test your learning regularly in the form of quizzes
Regularly testing what you've learned in a quiz format is a very effective way to anchor your anatomy knowledge. Quiz-style tests help you objectively grasp your level of understanding and areas you lack while repeating knowledge.
For example, by using a learning app to conduct quizzes every specific period, you can reconfirm what you've learned and strengthen your memory. There are a wide range of quiz formats, such as multiple choice questions, fill-in-the-blank questions, and short answer questions, and each helps understanding from a different angle and develops the ability to utilize various types of knowledge.
Get feedback
If possible, get feedback from other learners and experts. It helps you find your own gaps in understanding and areas for improvement. You can also keep yourself motivated to learn by regularly testing yourself. Feeling a sense of accomplishment and progress increases motivation for continuous learning.
summary
This time, I explained how to study “fingerdorsal aponeurosis” using an application!
Thank you for reading this far.
I would be happy if reading this article helped you learn about anatomy.
Learning is a long, never-ending journey, but I sincerely wish you all the best. Let's continue to study together and work hard for the national exam!
Please look forward to the next blog.




