beginning
In this article, I will explain effective study methods, starting with knowledge of specialized parts in human anatomy.
In human anatomy, it is necessary not only to memorize the names of various organs, muscles, and bones, but also to remember where they are located in the body. Therefore, it is necessary to learn as efficiently as possible.
I hope you can read this article and use the app to deepen your understanding even a little bit.
Now, I'll explain the details about the “tarsal bone” and how to study human anatomy.
teamLab Body Pro Free Download
A 3D anatomy app that shows all the structures of the human body
Download teamLab Body Pro here!
What is tarsal bone?
The anatomy application allows you to view a selection of anatomy 3D models. In this model, there are various observation methods such as surfaces, cross-sections, and nervous systems. This time, I'll explain using an anatomy application.
About tarsal bones
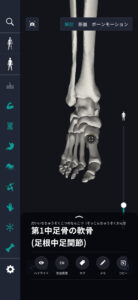
Study points
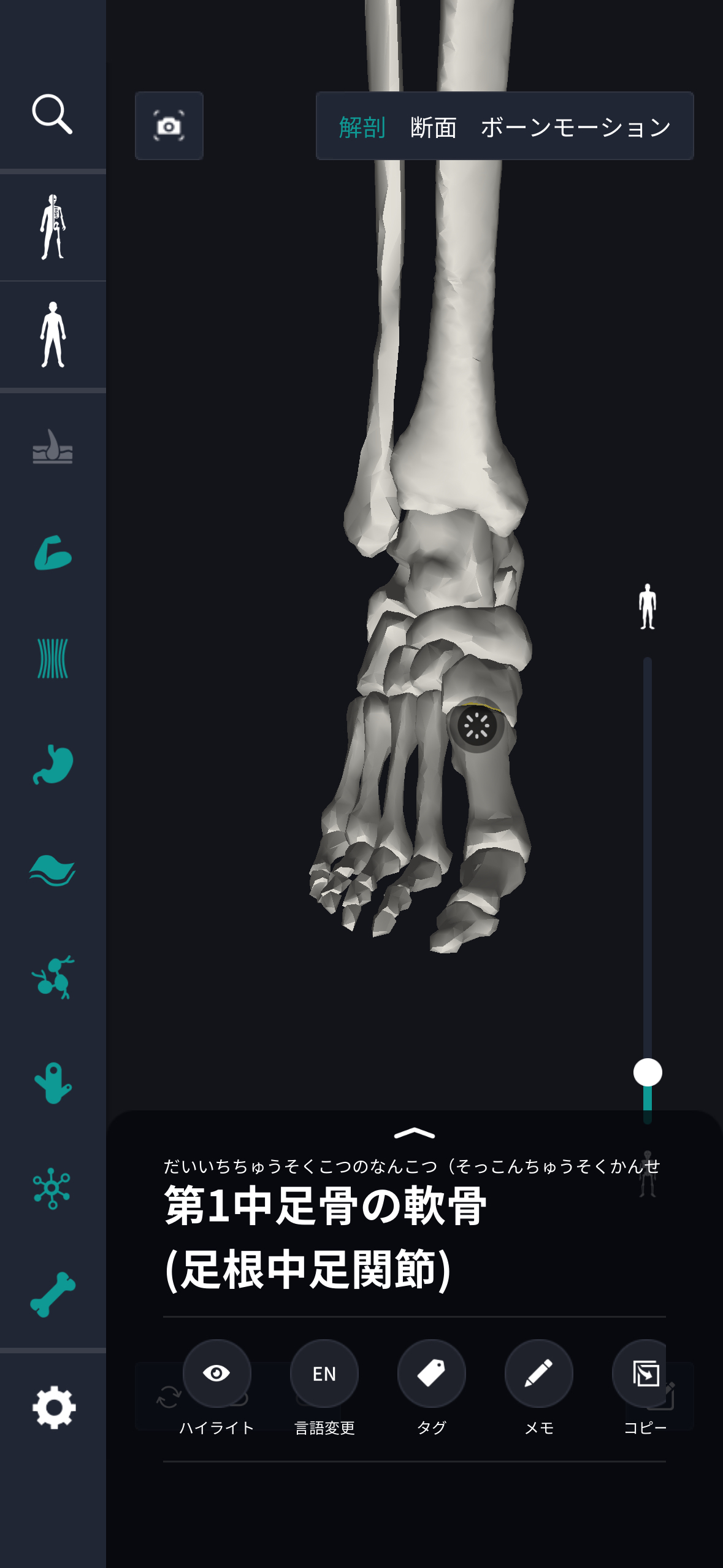
The location and structure of the tarsal bone
The location and structure of the tarsal bone is an important factor that directly affects the shape and function of the foot. The tarsal bone group is located below the ankle and at the top of the foot, and is closely related to each other to enable movement. Normally, it consists of 7 major bones from the ankle to the toe. It consists of the talus bone, heel bone, scaphoid bone, cubic bone, and three cuneiform bones. The talus bone is located in the articular part of the ankle and is connected to the tibia and fibula, providing mobility and stability. The heel bone is located at the back of the foot, supports the weight of the body and absorbs shock during walking. The scaphoid bone is located anterior to the talus bone and is important for arch formation. The cubic bone is on the side of the scaphoid bone and makes up the outside of the foot. There are three cuneiform bones, each arranged medially, midway, and outward, and supports the structure of the forefoot. The structure of the tarsal bone has a smooth surface adapted to form joints, and the connection between muscles and tendons enables flexible and elastic movement. These bones are held together tightly by ligaments, providing stability and strength. The arrangement and shape of the tarsal bones is designed to optimize overall foot movement and maintain balance during exercises such as walking, running, and jumping. The unique structure of each bone provides the flexibility and support needed for foot movement.
The role and function of tarsal bones
The tarsal bone is the main element that supports the structure of the foot, and its role and function play an important part in physical function. The tarsal bone performs three main functions: weight support, shock absorption, and flexibility and stability of foot movements, and each contributes to movement in daily life. First of all, the tarsal bones support the weight of the body. The calcaneus plays a particularly important role and holds weight stably while standing or walking. The talus bone and heel bone make up the back of the foot and support the body's center of gravity along with other tarsal bones. In turn, the tarsal bone effectively absorbs the impact of movement. The impact received from the ground while walking or running is absorbed by the heel bone and distributed to other tarsal bones. This prevents bones and joints from being overloaded. Finally, foot movement requires flexibility and stability. The scaphoid and cuneiform bones form the arch of the foot, and this structure enables flexible movement and balance of the foot. These bones work together to maintain the natural curve of the foot and make walking more efficient. The role and function of tarsal bones is essential in daily life activities, and by moving these bones in harmony, the overall function of the foot is maximized. Thus, the tarsal bone is the foundation that supports the motor function of the body.
English notation for tarsal bone
I will explain the English notation for tarsal bone. The tarsal bones are an important part of the human body's skeleton, and their bone group is usually called “Tarsal Bones” in English. These bones are composed of 7 bones, and while each has a different role, they cooperate to support foot movement. Specifically, the talus bone is called “Talus,” and the calcaneus is expressed as “Calcaneus.” The talus bone plays an important role in the ankle joint, and the heel bone forms the heel structure. The scaphoid bone is called the “Navicular Bone” and supports the arch of the foot. The cubic bone is known as the “Cuboid Bone” and contributes to the outer structure of the foot. Furthermore, each of the three cuneiform bones is called “Cuneiform Bones,” and they are specifically named “medial (inner) Cuneiform,” “Intermediate (intermediate) Cuneiform,” and “Lateral (outer) Cuneiform.” These bones reinforce the foot's structure and provide flexibility and stability. These English names are used internationally in the field of anatomy, and they are a basic language for understanding the foot skeleton. Each name of tarsal bone is named based on its function and position, and there is an academically consistent expression. This makes it possible to gain a common understanding around the world.
How to study human anatomy
I will explain specific study methods using human anatomy applications.
Check your past learning history and practice repeatedly
Here are the steps to check your anatomy learning history and practice iteratively effectively.
1. Check your learning history in the app
Reviewing your learning history with the application is an important step in effectively advancing anatomy learning. First, launch the app and go to the learning history section from the main menu. Many anatomy apps are designed to show your progress in the form of graphs and lists, so you can visually check which parts you've learned about and how much time you've spent.
By using this data, you can understand which areas you have strengths in and where you need to spend more time and effort. We also recommend using a dedicated tag or notebook function to mark areas you are particularly weak at or where you need to relearn. Regularly checking your learning history and looking back on past learning content will lead to efficient review and deepening understanding.
2.Make a plan for iterative learning
Making an efficient repetitive learning plan based on learning history is extremely effective in promoting knowledge retention. First, identify weak points and areas where you need to relearn. Next, arrange these study items into a weekly or monthly calendar and create a specific study schedule. By proceeding in a planned manner, you can learn each part evenly and avoid packing in a large amount of information at once.
Using a task management app or digital calendar to set study reminders is effective. Also, it's important to have the flexibility to regularly review progress and revise plans as needed. By having goals and proceeding with your studies in a planned manner, you can efficiently acquire anatomical knowledge.
3.Use 3D features to learn visually
By utilizing the 3D function, learning anatomy is easier to understand visually. The 3D model shows the structure of the human body three-dimensionally, and each part can be observed in detail. This makes it possible to intuitively grasp positional relationships between deep muscles and organs that are difficult to capture in a planar view. For example, you can learn even the smallest details by rotating specific muscles and bones and zooming in and out.
Also, there are many apps that have the function of displaying cross-sectional views of each part using a 3D model, which is useful for deepening understanding of internal structures. This diversity of visual information helps with memory retention and improves immediate responsiveness in tests and practice situations. By utilizing the 3D function and learning visually, you can learn anatomy knowledge more deeply and efficiently.
Use the memo function concretely
Test your learning regularly in the form of quizzes
Regularly testing what you've learned in a quiz format is a very effective way to anchor your anatomy knowledge. Quiz-style tests help you objectively grasp your level of understanding and areas you lack while repeating knowledge.
For example, by using a learning app to conduct quizzes every specific period, you can reconfirm what you've learned and strengthen your memory. There are a wide range of quiz formats, such as multiple choice questions, fill-in-the-blank questions, and short answer questions, and each helps understanding from a different angle and develops the ability to utilize various types of knowledge.
Get feedback
If possible, get feedback from other learners and experts. It helps you find your own gaps in understanding and areas for improvement. You can also keep yourself motivated to learn by regularly testing yourself. Feeling a sense of accomplishment and progress increases motivation for continuous learning.
summary
This time, I explained how to study “tarsal bones” using an application!
Thank you for reading this far.
I would be happy if reading this article helped you learn about anatomy.
Learning is a long, never-ending journey, but I sincerely wish you all the best. Let's continue to study together and work hard for the national exam!
Please look forward to the next blog.